What Is The Difference Between AC And Refrigeration?
Air conditioning and refrigeration systems are essential cooling technologies that shape the comfort and safety of modern living. While they both rely on similar thermodynamic principles, their purposes, designs, and operating conditions differ significantly. Whether you are a homeowner trying to understand your AC unit or a business owner evaluating refrigeration systems for your facility, knowing these differences can help you make the right choice for your needs.
Understanding Refrigeration Systems
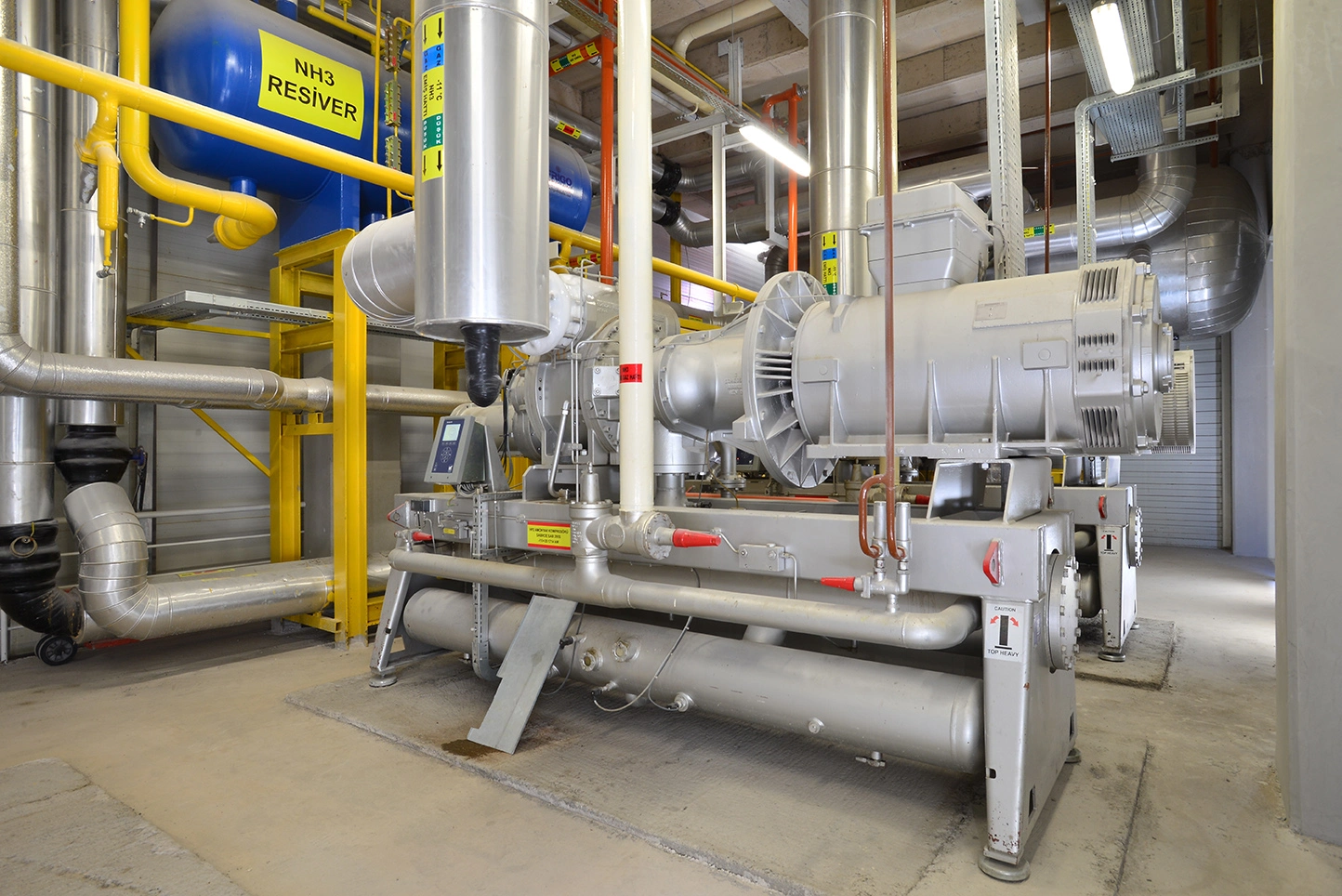
Refrigeration systems are designed to remove heat from a specific enclosed space and maintain a constant, often very low, temperature. They are widely used in industries where temperature-sensitive products need preservation, such as food storage, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing.
A refrigeration system works by circulating refrigerant through a closed loop, absorbing heat inside the refrigerated space and releasing it outside. These systems are engineered to deliver stable and precise temperature control, sometimes reaching well below freezing. This makes them essential for preserving perishable goods and maintaining product quality over time.
What Is Air Conditioning?
Air conditioning, or AC, is a comfort cooling solution intended to regulate the indoor environment of residential, commercial, or industrial spaces. While it also removes heat from the air, the goal is not extreme temperature reduction but rather maintaining a comfortable range—usually between 20°C and 25°C.
AC systems also help in controlling humidity and improving air quality through filtration. This makes them ideal for living spaces, offices, and other places where human comfort is the priority.
Key Differences Between AC and Refrigeration Systems
The main difference between AC and refrigeration systems lies in their application and temperature control range. Air conditioning is about comfort; refrigeration is about preservation. An AC system will cool a space enough for people to feel comfortable, while a refrigeration system may be required to maintain a storage room at -18°C for frozen goods.
The refrigerants used can also differ. Some refrigerants are optimized for ultra-low temperatures in refrigeration systems, while others are designed for moderate cooling in air conditioning. Additionally, the insulation and construction requirements for refrigeration units are far more rigorous because any temperature fluctuation can affect stored goods.
How Both Systems Work
Both AC and refrigeration operate on the vapor-compression cycle. This involves compressing a refrigerant gas, condensing it into a liquid, expanding it to lower the temperature, and evaporating it to absorb heat. The cycle repeats continuously, removing unwanted heat from the target space.
However, while AC systems prioritize airflow and distribution across large open spaces, refrigeration systems focus on sealing and isolating the cooled area to prevent heat intrusion.
Temperature Control and Precision
Refrigeration systems are designed for precision. For example, a pharmaceutical cold room may need to maintain exactly 4°C, with minimal deviation. Air conditioning systems do not require such exact control; a small variation in room temperature is not a major issue for human comfort. This difference in precision explains why refrigeration systems often use advanced thermostats and monitoring devices.
Applications in Different Industries
Refrigeration systems are critical for food storage, beverage processing, cold chain logistics, and medical facilities. Without them, supermarkets could not keep dairy, meat, and frozen products safe for consumption.
Air conditioning, on the other hand, dominates in residential and office environments, retail spaces, hotels, and public transportation. In some cases, large commercial buildings use combined systems that integrate both AC and refrigeration technologies.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Energy efficiency plays a crucial role in both systems, but it is measured differently. AC efficiency is usually rated by the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER), while refrigeration efficiency is measured in terms of Coefficient of Performance (COP). Refrigeration systems generally require more insulation and may operate continuously, leading to different energy usage patterns compared to AC systems, which may cycle on and off depending on the room temperature.
Maintenance Needs
Both AC and refrigeration systems require regular maintenance to function efficiently. Refrigeration systems often require more frequent inspections due to their critical role in product preservation. A small fault in a refrigeration unit can lead to costly product losses, whereas an AC fault primarily impacts comfort.
Maintenance includes cleaning coils, checking refrigerant levels, inspecting electrical components, and ensuring that seals and insulation remain intact.
Environmental Impact
The choice of refrigerant in both systems impacts the environment. Older refrigerants with high ozone depletion potential have been phased out in favor of more eco-friendly alternatives. Modern refrigeration systems often use low-GWP (Global Warming Potential) refrigerants, while AC units increasingly incorporate inverter technology to improve energy efficiency.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
If your goal is to maintain comfort in a living or working space, an AC system is the right choice. However, if you need to preserve goods at a specific low temperature, a dedicated refrigeration system is essential. Businesses such as restaurants, grocery stores, and hospitals cannot rely on AC alone for their cooling requirements—they must invest in specialized refrigeration solutions.
Refrigeration Systems in the Future
The future of refrigeration systems involves advanced technologies such as IoT monitoring, AI-based temperature control, and the use of natural refrigerants to minimize environmental impact. Similarly, air conditioning is moving toward smart home integration, allowing for better energy management and customization.
Conclusion
While AC and refrigeration systems share scientific principles, their differences in application, temperature control, and design are significant. Air conditioning is all about comfort, whereas refrigeration systems ensure the safe storage and preservation of goods. Understanding these distinctions will help you select the right system for your specific needs, whether for your home, business, or industrial facility.